In today's drone flying community, the First-Person View (FPV) experience is becoming increasingly popular. Whether you're a professional racing pilot or a hobbyist who loves aerial photography, everyone wants to achieve clear and stable real-time video transmission through high-quality FPV equipment. This allows for better drone control and the ability to capture amazing moments. Today, let's take a closer look at three exceptional FPV devices: the RFVTX-T67 (6–7GHz Transmitter), the RFVRX-R67 (6–7GHz Receiver), and the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX (Dual-Band Transmitter). Discover how they can enhance your flying journey.
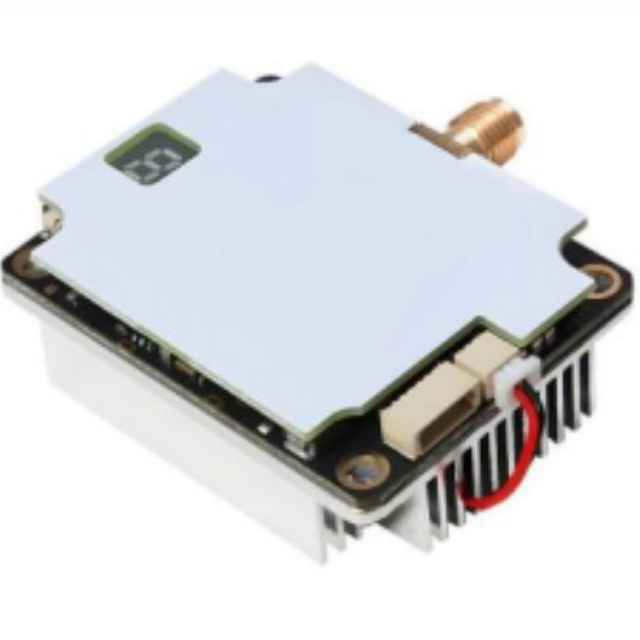
RFVTX-T67: The Powerful 6–7GHz Transmitter
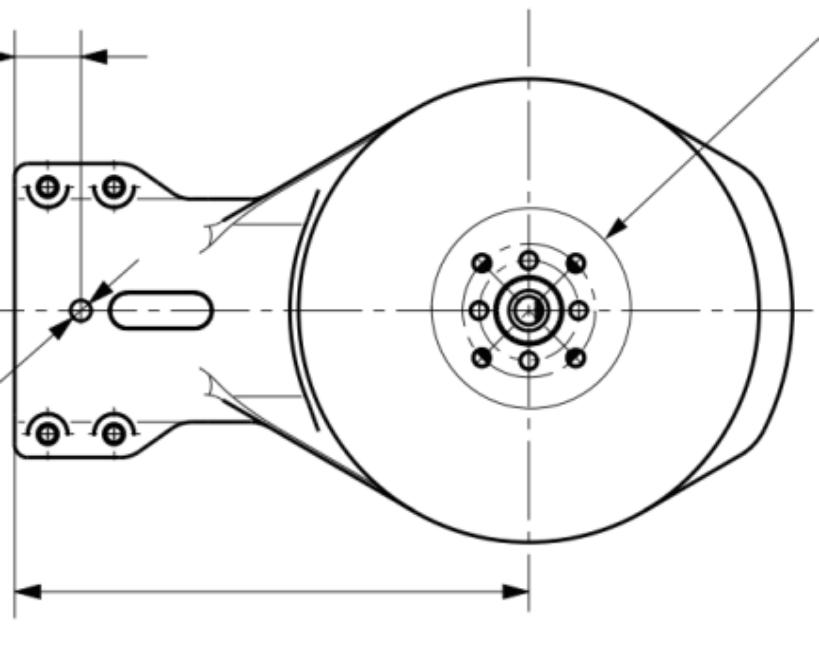
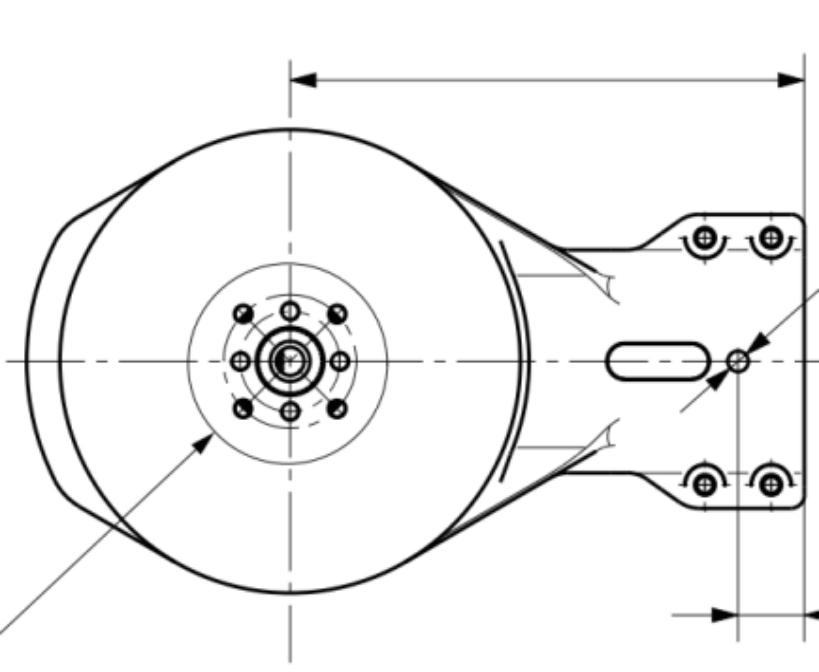
The RFVTX-T67 is a 6–7GHz transmitter designed specifically for FPV enthusiasts who demand top performance. With 64 selectable channels, it can easily handle complex and varied flying environments, effectively avoiding signal interference and ensuring stable and smooth video transmission no matter where you fly. Its power is adjustable between 25–3000mW, catering to both close-range precision control and long-range exploration. Moreover, this transmitter is equipped with an efficient cooling fan and an SMA connector, along with an intuitive on-screen menu that makes setup a breeze, eliminating any worries about complicated procedures.
Imagine yourself in an intense FPV racing competition, maneuvering your drone through narrow tracks where every turn and obstacle requires precise judgment and quick reactions. At such moments, the RFVTX-T67, with its robust signal transmission capabilities and stable performance, delivers high-definition footage in real-time to your display. It makes you feel as if you're inside the drone, experiencing the perfect blend of speed and excitement. Whether it's the slightest vibrations during high-speed flight or the breathtaking panoramic views from a distance, everything is clearly presented before your eyes, giving you an edge in the race and helping you easily overtake your opponents.
RFVRX-R67: The High-Sensitivity 6–7GHz Receiver
The perfect match for the RFVTX-T67 is the RFVRX-R67, a 6–7GHz video receiver. It has 40 channels that can accurately receive signals from the transmitter, ensuring stable and smooth video transmission. With a sensitivity of -96dBm, it can capture even the weakest signals, providing you with clear images. Moreover, this receiver boasts a frequency stability of ±100kHz and a wide input voltage range of +7–28V, allowing it to maintain excellent performance during long-range transmission and providing reliable support for your FPV flights.
When you're flying outdoors, you may encounter various complex terrains and environmental factors, such as mountains and building obstructions, which can interfere with signal transmission. However, the RFVRX-R67, with its outstanding performance, can easily tackle these challenges. It can stably receive signals from the transmitter in various complex environments, eliminating concerns about signal loss or video lag during flight. Whether you're flying between urban skyscrapers or exploring vast fields and forests, the RFVRX-R67 delivers clear and stable images, allowing you to fully enjoy the pleasure of flying.
4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX: The Versatile Dual-Band Transmitter
In addition to the 6–7GHz devices, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX dual-band transmitter offers even more options for your FPV flights. This transmitter supports both the 4.9GHz and 5.8GHz bands, with 8+48 channels available, meeting the diverse needs of different users in various scenarios. Its maximum power output of 2.5W provides longer transmission distances and stronger signal penetration, enabling you to freely explore broader areas during your flights.
The 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX employs the advanced IRC Tramp protocol to ensure efficient and stable signal transmission. It also features an SMA connector and an aluminum casing, along with an efficient cooling fan. These components not only ensure stable operation over extended periods but also enhance the device's durability and longevity. Whether you need to fly at low altitudes in urban areas or explore high-altitude regions in the mountains, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX will provide reliable signal transmission support, making your flights more effortless and enjoyable.
Combining These Devices for the Ultimate FPV Experience
These three devices not only have outstanding individual performance but also create a powerful synergy when used together. You can pair the RFVTX-T67 with the RFVRX-R67 to form a complete 6–7GHz FPV transmission system, enjoying stable and high-definition video transmission. When you need broader frequency coverage, the 4.9/5.8GHz 2.5W VTX offers more options, allowing you to switch frequencies flexibly according to different flight scenarios to achieve the best possible signal transmission.
Whether you're participating in professional FPV racing competitions or exploring with aerial photography in your spare time, these three devices can meet your needs. Their high performance and stability will bring you an unparalleled flying experience, allowing you to soar freely in the sky and capture every amazing moment. Choose these devices to embark on your professional FPV flight journey and make every flight an unforgettable memory.