Products
- Capacitor Networks, Arrays(2073)
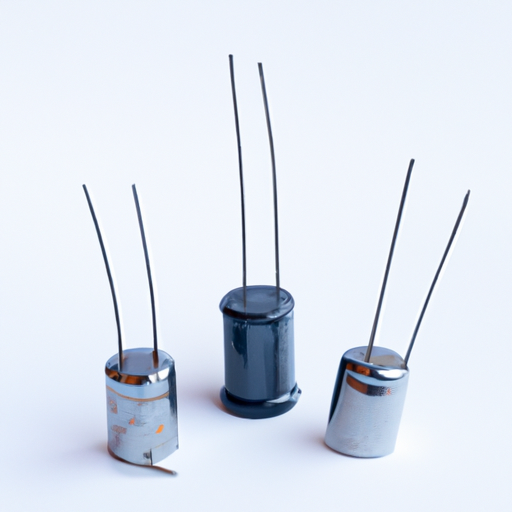
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors(119232)
- Tantalum Capacitors(106098)
- Ceramic Capacitors(802073)
- Electric Double Layer Capacitors (EDLC), Supercapacitors(2508)
- Film Capacitors(165215)
- Accessories(256)
- Mica and PTFE Capacitors(9477)
- Trimmers, Variable Capacitors(1755)
- Thin Film Capacitors(3401)
- Fuses(23615)
- Fuseholders(6012)
- Varistors, MOVs(15992)
- Gas Discharge Tube Arresters (GDT)(3698)
- Circuit Breakers(115397)
- Circuit Protection Accessories(5100)
- Thermal Cutoffs (Thermal Fuses)(413)
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)(811)
- PTC Resettable Fuses(5024)
- Inrush Current Limiters (ICL)(1291)

 Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)
Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)
 Endress+Hauser
Endress+Hauser
 Pepperl+Fuchs
Pepperl+Fuchs
 PMDM
PMDM
 YAGEO
YAGEO
 EMIT
EMIT